-
Salpingitis In Cats
Salpingitis, defined as inflammation of the uterine tube is often associated with endometritis or pyometra, and probably occurs more commonly than is reported as a cause of breeding problems in female cats[1]. Because it is assumed to be an ascending infection, the agents are probably the same as those causing endometritis, but studies are lacking. Anecdotal evidence of Citrobacter […]
-
Citrobacter spp
Citrobacter spp are Gram-negative enteric coliform bacteria that can cause vaginitis and salpingitis in the cat[1]. C. freundii and C diversus are enterobacteria commonly isolated from soil, water, sewage, and food as well as from different organs of diseased and healthy animals, including mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians in which it is considered to be an opportunistic or secondary pathogen[2]. In humans, this […]
-
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctitivis is a common eye disease of cats, defined as an inflammation of the conjunctival membranes surrounding the eye, is a very common disease in cats. There are a wide range of causes including allergies, scratches from other cats and objects, autoimmune diseases (eosinophilic granuloma complex), viral infections (FHV, FCV and rarely FIP), bacteria (Chlamydia) and other parasite infections such […]
-
Bacterial diseases in Cats
Bacterial diseases affect all animals and cats are no less immune or unique to their onslaught. They can cause varying ranges of illness in cats from mild dermatitis to sepsis and death. Appropriate antimicrobial therapy should be based on isolation and culture and sensitivity of causative bacteria. Common bacterial diseases in cats include: Actinobacillus spp – gingivitis and respiratory infections […]
-
Cleft palate
“Hair lips” and “cleft palate” are a genetic disorder common to all animals, including the cat. It is caused by failure of closure of the palatal mucoperiosteum during fetal development in utero. The deficit in the hard palate can range in severity from mild to severe. There may be loss of tissue in the hard […]
-
Cat Anatomy
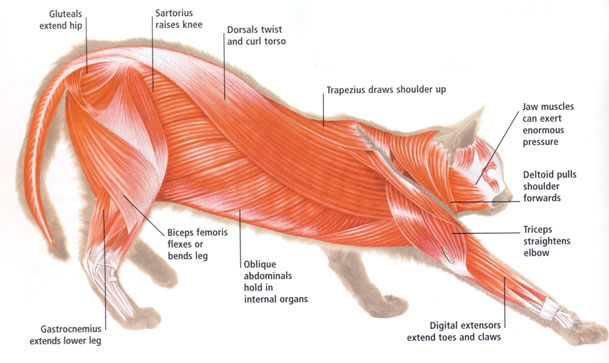
General feline anatomy Anatomical abnormalities Bracyury (Short tail) Cleft palate Cryptorchidism (retained testicle) Cutaneous asthenia Flat chest syndrome (kittens) Hip dysplasia Hydrocephalus 1. calcaneus 2. carpals 3. caudal vertebrae 4. cervical vertebrae 5. clavicle 6. costal cartilage #5 7. femur 8. fibula 9. humerus 10. hyoid apparatus 11. ilium 12. ischium 13. lumbar vertebrae 14. […]
-
Organophosphates
Organophosphate (OP) poisoning are the most frequently reported of all toxins affecting cats, due primarily to the abundance of OP-based flea collars, flea rinse and other insecticidal preparations used by households on pets. Farm cats have also been reported with OP poisoning in areas where OPs are used to spray farmland[1]. Proprietary formulations include Malathion, parathion, Diazinon, […]
-
In practise
Are You Delivering and Communicating Value?[1] According to the November 2009 issue of Money magazine, veterinarians were ranked fourth on the list of jobs likely to grow in 10 years in the United States, and pet ownership has increased 17% in the past 10 years. Thanks to recent national surveys, as well as materials made […]
-
Quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) refers to a standard of physical and social behaviour commensurate to what is expected for a particular cat’s age and social location. QOL embraces the five freedoms that minimizes physical and psychological stress, and is a matter of consideration when euthanasia is being contemplated due to disease, abandonment and possibility of restoring a cat’s physical […]
-
Recognition and assessment of pain
Recognizing pain is the cornerstone of effective pain management in veterinary practice. Recognizing pain in animals is not intuitive, particularly by individuals unfamiliar with normal behavior for a species or individual. Numerous factors complicate the evaluation of pain in animals. Any pain scale should consider the following characteristics: species, breed, environment and rearing conditions, age, gender, cause […]