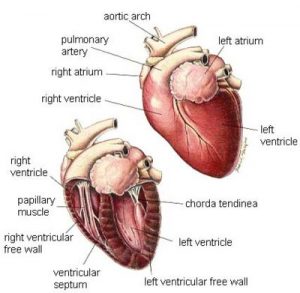
 Heart disease in cats is relatively common.
Heart disease in cats is relatively common.
One of the most challenging aspects of feline heart disease is that cats may not show any warning signs (such as exercise intolerance, coughing, weakness) until the process is very advanced. Untreated heart disease can lead to congestive heart failure and death.
The most common heart disease in cats is cardiomyopathy, often diagnosed as a heart murmur. These are often detected at a young age, during routine vaccinations.
Diagnosis
- Chest Radiographs (x-rays)
Chest radiographs are important components in the diagnosis of feline heart disease. A diseased heart will most often enlarge over time. In advanced stages, fluid may be detectable in the chest cavity (pleural effusion) or in the lungs themselves (pulmonary edema).
- Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)
An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a tracing of the electrical activity of the heart. It documents heart rate and rhythm. In addition, subtle changes can occur in the shape of the ECG spikes that can reveal certain types of pathological changes in the heart. It is a rapid and painless test that can be performed right in the veterinary office.
- Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram, also known as a cardiac ultrasound exam, is one of the most advanced and sensitive tests for determining the presence of heart disease in animals. It is painless and generally does not require sedation. The technique uses sound waves to actually visualize the heart in action. From this exam, the dimensions of each heart chamber can be determined.
- Sinus rhythm and sinus tachycardia
In normal healthy cats, a normal heart rate of 140 beats per minute is normal. Also, there is usually a normal sinus rhythm is defined as having regularly spaced P waves (<10% P-P variation), and for every P wave, there is a corresponding QRS complex followed by a T wave on an ECG. Once a heart rate exceeds 200 beats per minute, a sinus tachycardia is more appropriate.
- Sinus bradycardia
Sinus bradycardia is defined as a heart rate below 120-140 beats per minute.
- Sinus arrhythmia
Sinus arrhythmia is any abnormal ECG rhythm in cats, where there is a gradual variation in P-P intervals that exceeds 10%, which is often associated with respiration. It is often associated with diseases that affect vagal nerve tone, including intracranial disease, elevated intraocular pressure (e.g. glaucoma) and primary respiratory disease.
Common heart diseases of cats
| Aortic (Sub-aortic) stenosis | Double-outlet right ventricle | Pericardial effusion | Third degree AV block |
| Atrial fibrillation | Double-chambered right ventricle | Peritoneal-pericardial diaphragmatic hernia | Tricuspid valve dysplasia |
| Atrial septal defects | Endocarditis | Pulmonary artery stenosis | Truncus arteriosus |
| Atrial standstill | FIP-induced pericarditis | Pulmonic valve stenosis | Toxoplasma pericarditis |
| Atrial tachycardia | Heart failure | Renal failure | Valvular endocardiosis |
| Atrioventricular septal defects | Heartworm disease | Second degree AV block | Ventricular tachycardia |
| Aortic thromboembolism | Hemoplasmas | Sinus bradycardia | Ventricular premature beats |
| Bacterial pericarditis | Hyperthyroidism | Sinus tachycardia | Ventricular septal defect |
| Cardiomyopathy – dilated | Hypertension | Supravalvular mitral stenosis and cor triatriatum sinister | Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome |
| Cardiomyopathy – hypertrophic | Hyperthyroidism | Supraventricular premature beats | |
| Cardiomyopathy – restrictive | Mitral valve dysplasia | Supraventricular tachycardia | |
| Chemodectoma | Mediastinal lymphoma | Tetralogy of Fallot | |
| Chylous effusion | Myocarditis | Patent ductus arteriosus | |
| Dissecting aneurysm | Pericardial cysts |